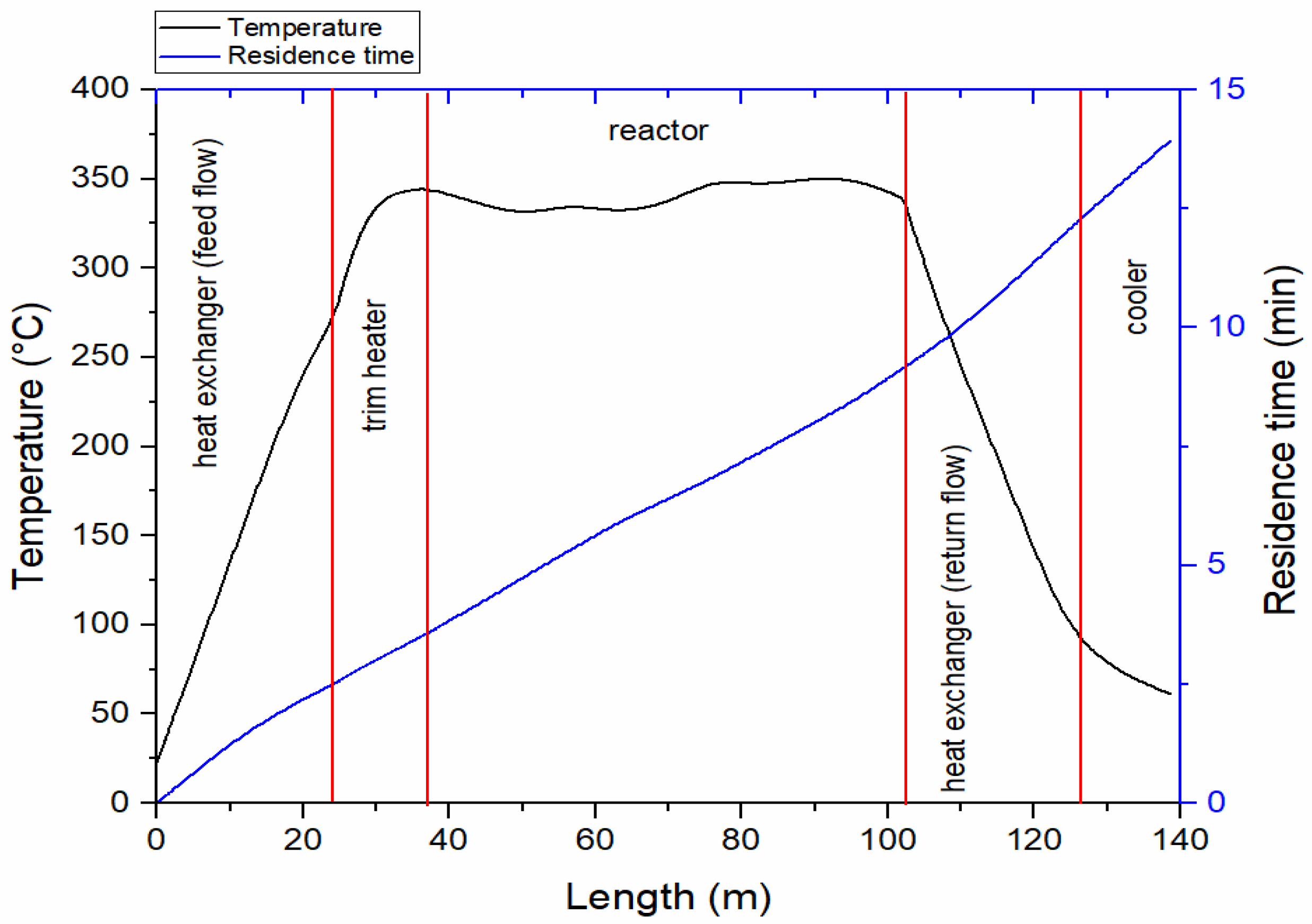
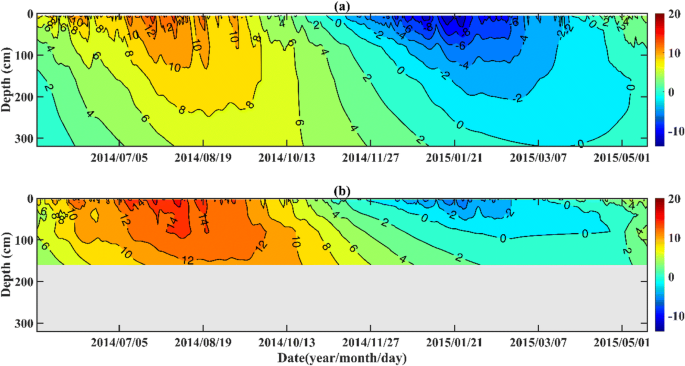
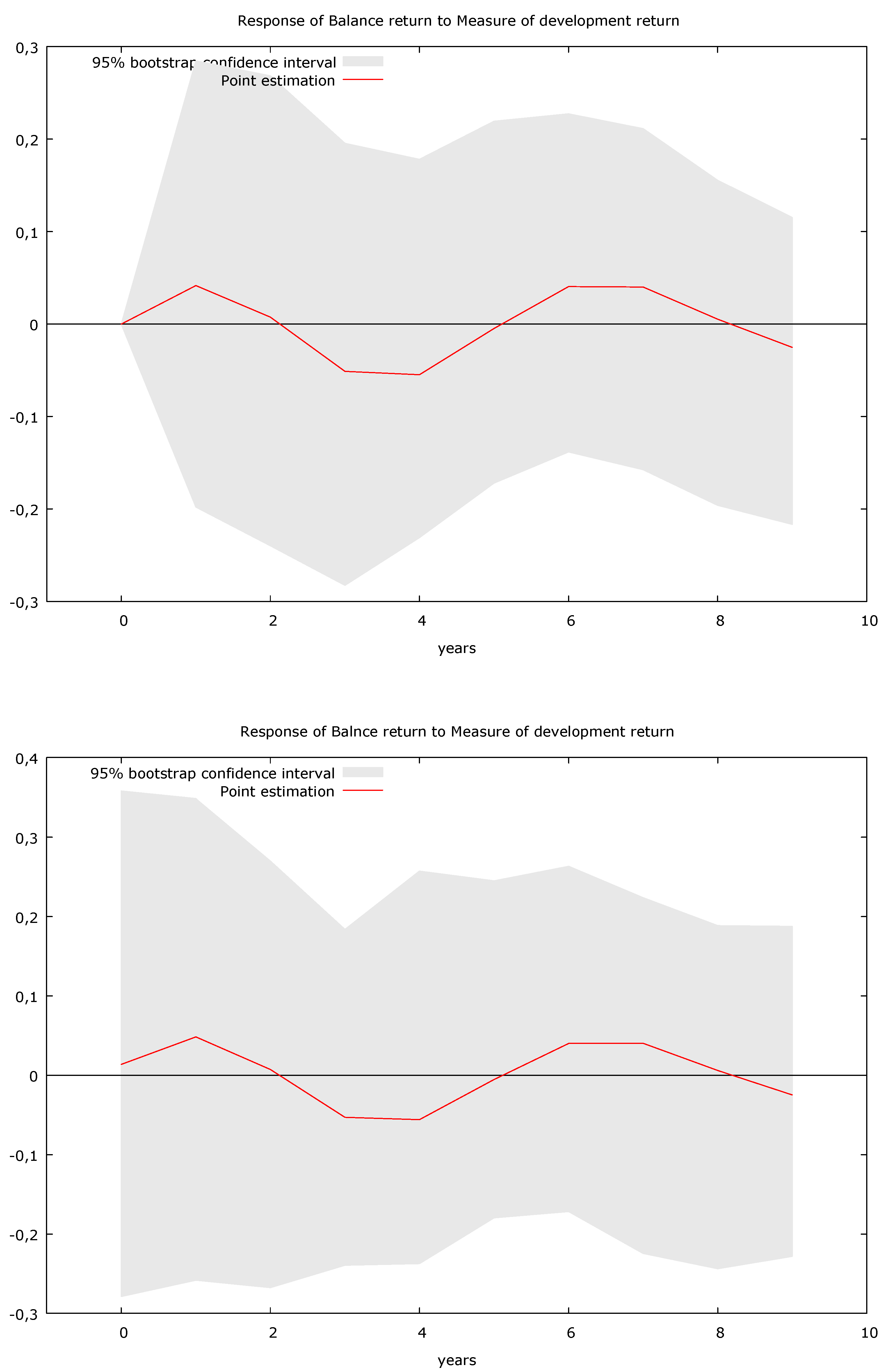
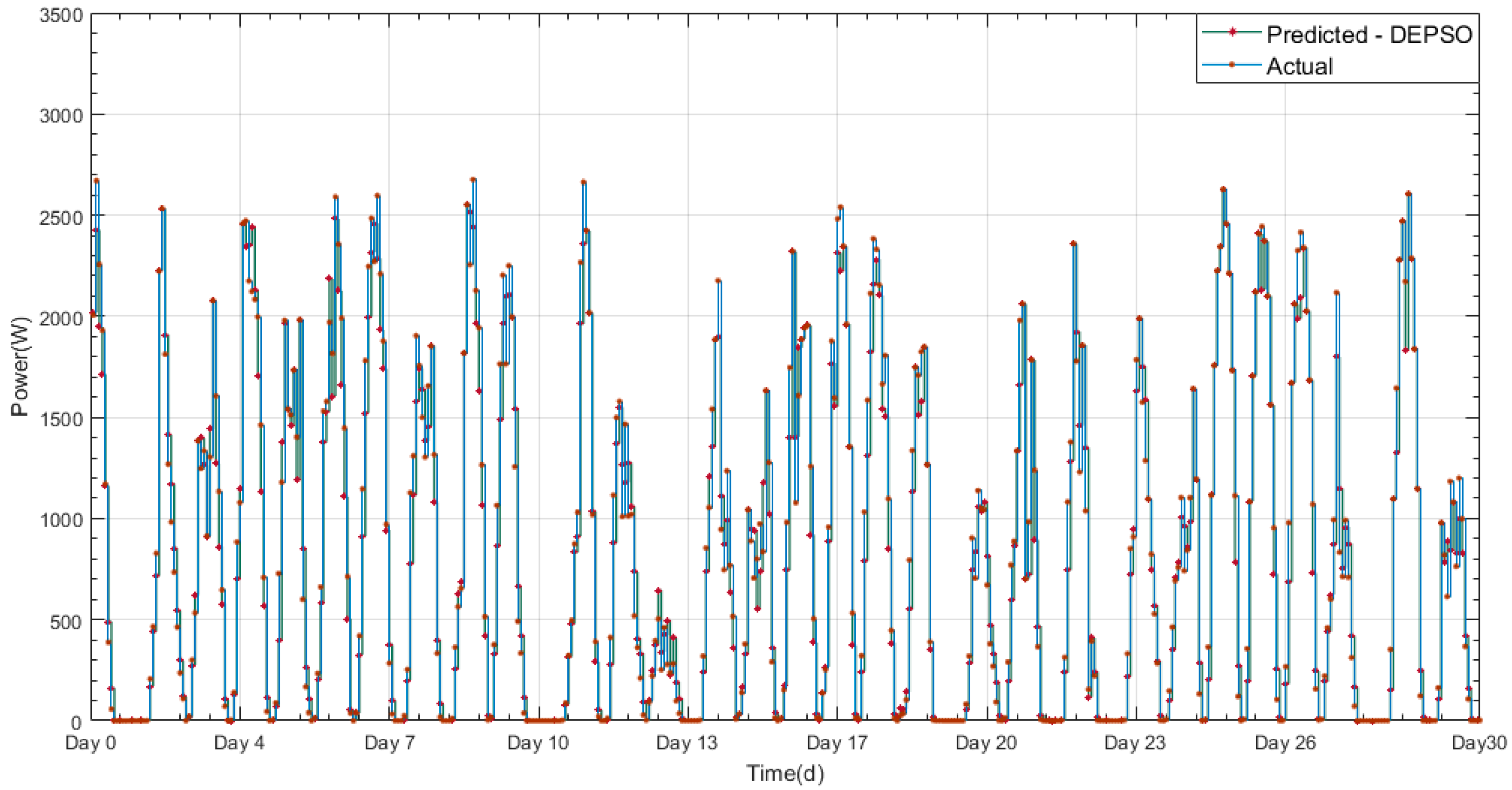
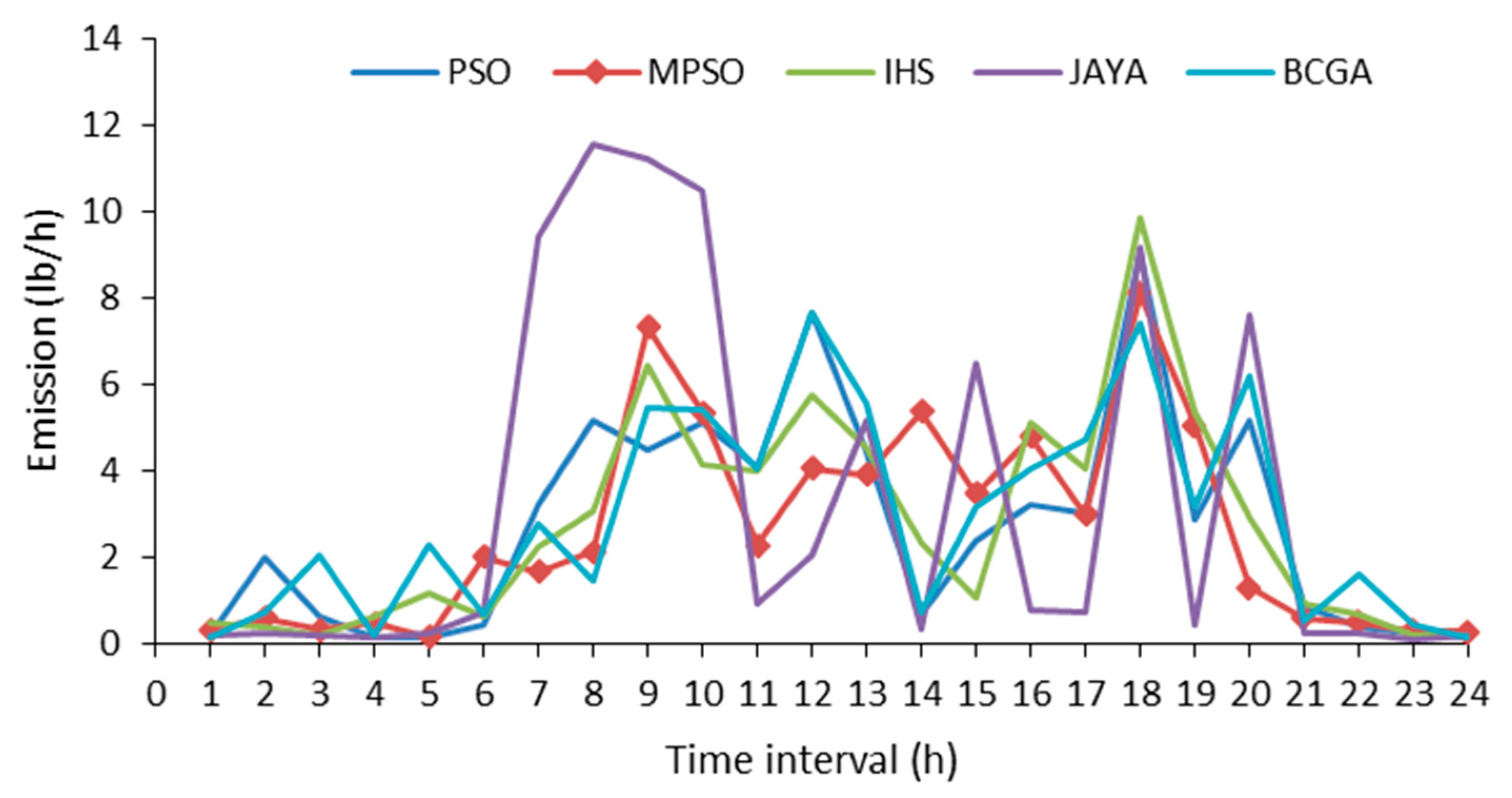
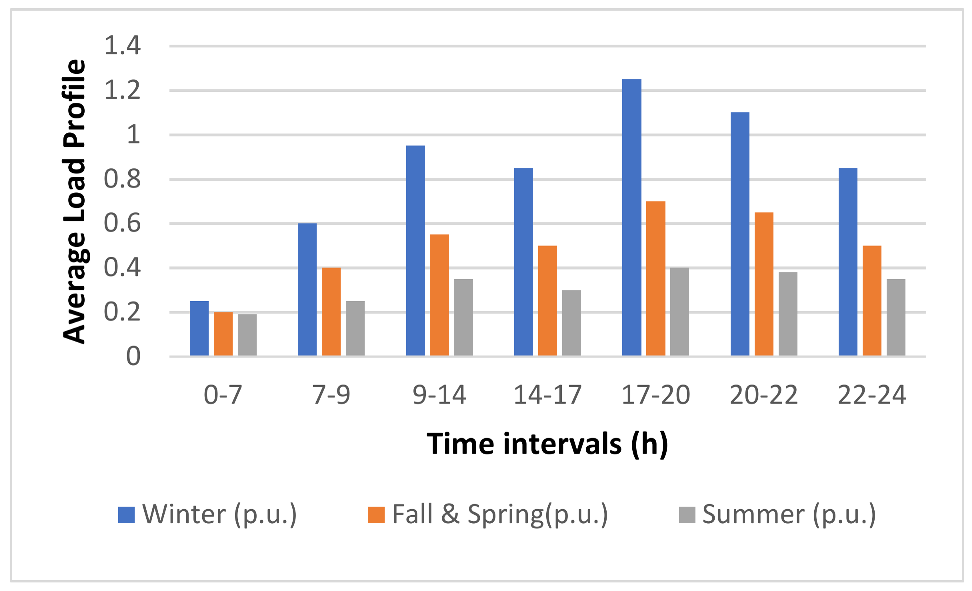
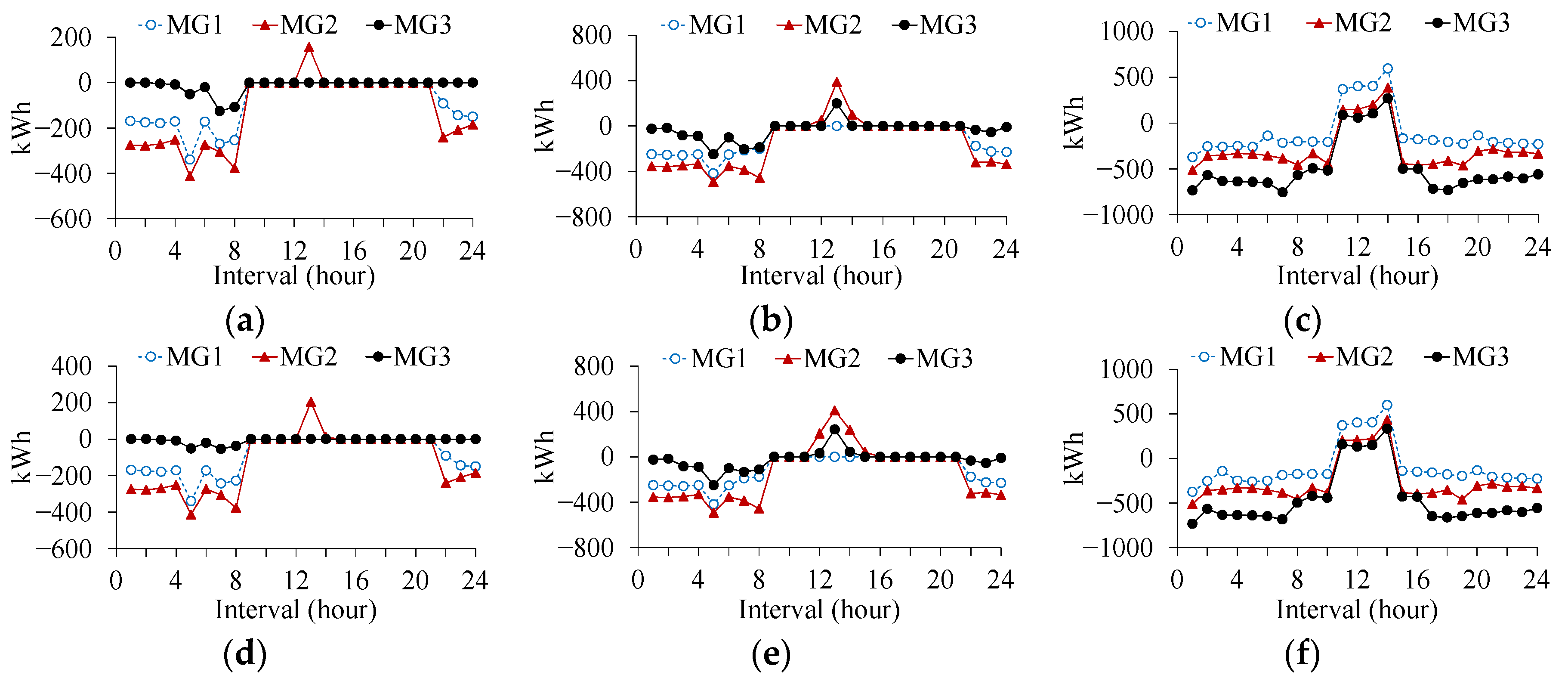
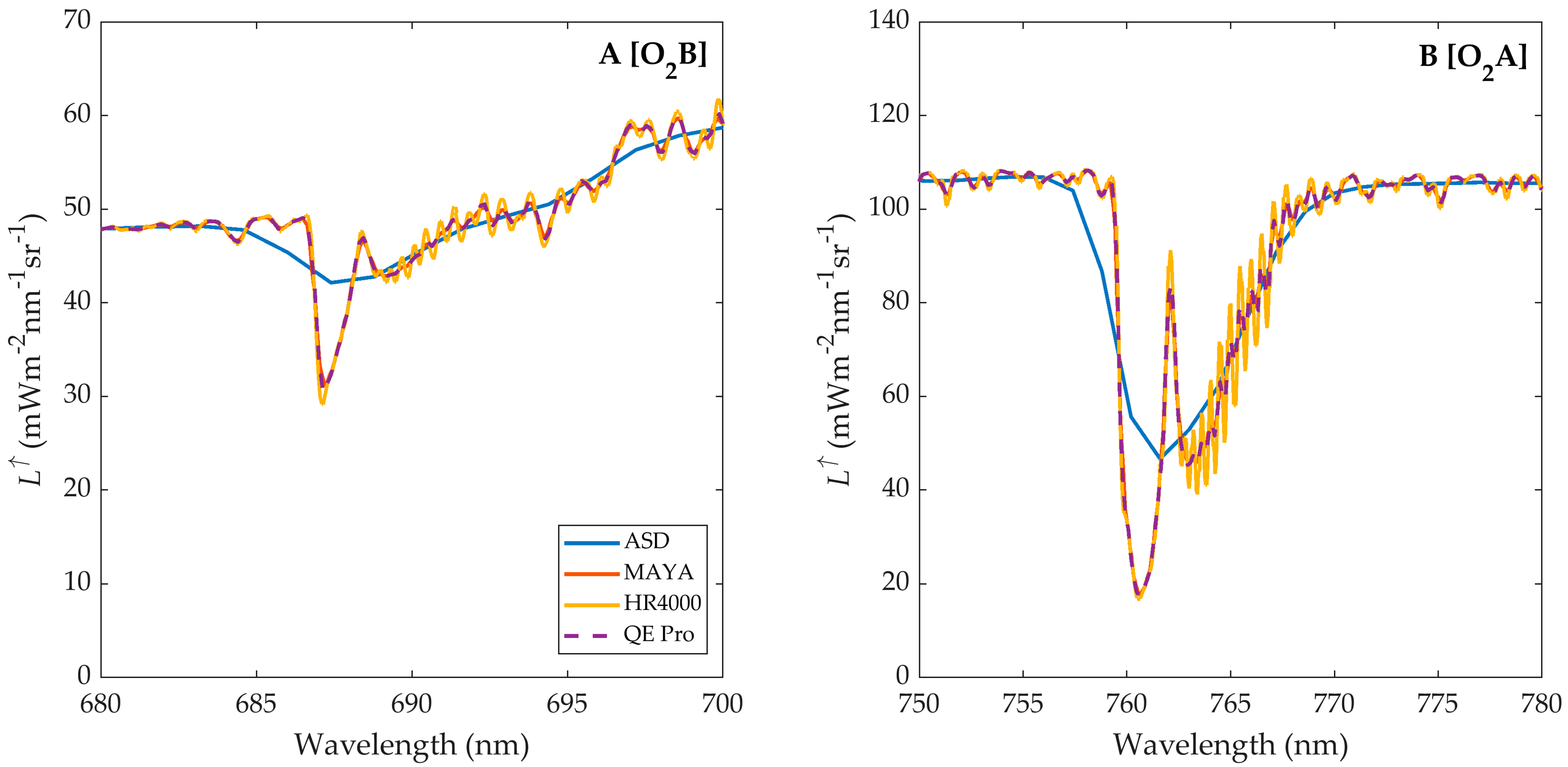
In addition measurements using equipment on nimbus 7 demonstrated the solar flux variation i e.
The solar constant varies over time on a regular 11 year interval because of.
These measurements show that the solar constant is not constant.
At time 1 the sun and a certain distant star are both overhead.
At time 2 the planet has rotated 360 and the distant star is overhead again 1 2 one sidereal day.
For the influ ence on the atmospheric energy budget time scales longer than a few days become important for climate research information over years to decades is needed.
The sun itself is known to have a slight variability to its radiation levels over 11 year cycles of 0 2.
The solar constant varies over time scales from minutes to years and decades.
Space based observations of solar irradiance started in 1978.
Calculation of elapsed time by the apparent position of the sun on a prograde planet like the earth the sidereal day is shorter than the solar day.
Since then sunspot number have risen and fallen in a regular 11 year cycle.
It is more difficult to prove the existence of the variation in the solar constant over a longer time interval for example with the 80 90 year gleissberg.
In 2012 an astronomical unit was defined as a specific length that being 149 597870700 million km or for practical purposes 150 million km.
The solar constant so variation during the 21st and 22nd solar cycles kyle et al 1993.
When going further back in time one has to rely on irradiance reconstructions using sunspots for the past 400 years or cosmogenic radionuclides for going back 10 000 years.
But it is not until a little later at time 3 that the sun is overhead.
The distance between the nucleus of the sun and the center of the mass of the solar system is not constant and varies from one cycle to the next.
An 11 year running average shows only the long term variation which shows a rise in total sunspot numbers from 1700 until today.
Modulation of the intensity of the 11 year sunspot cycle by the 90.
This along with a 10 increase in the solar constant every 10 000 000 000 years can have dramatic impacts on earth s climate in regional areas such as the sea or on a global basis over time.
The sun s temper varies on an 11 year cycle typically taking about 5 1 2 years to move from the quieter period of solar minimum to the more turbulent solar maximum.
In a january 17 2003 article email protected describes the extent of the fluctuations in solar radiation over time how.
It varies with the 11 year sunspot solar cycle.
The solar constant is a measure of the total solar energy flux integrated across all wavelengths of radiation two decades of satellite observations reveal that the solar constant varies over time scales of days to a decade and there does appear to be a significant relationship with the sunspot number cycle.